
Lumbar puncture (LP) demonstrated elevated protein and a positive venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) titer of 1:4. The infectious disease service was consulted, and neuroimaging was unremarkable. The patient was admitted to the hospital for further workup and treatment. The syphilis screen was also positive, with a rapid plasma reagin titer greater than 1:256. The HIV screen returned positive, and HIV 1 Ab/Ag was reactive, with a total CD4 count of 61 cells/μL. A diagnostic workup was ordered for syphilis, HIV, Lyme disease, and toxoplasmosis screening.

There was concern regarding possible acute retinal necrosis, so the patient underwent a diagnostic tap with intravitreal injection of 400 µm ganciclovir (Zirgan Bausch + Lomb).

The differential diagnosis in this young, otherwise healthy patient included acute retinal necrosis, syphilis, Lyme disease, and toxoplasmosis. Fundus photography OS shows superior peripheral atrophic retina (A) with ischemic vessels (B). Fundus photograph taken 10 days after treatment demonstrates improvement in vitritis and retinitis OS.įigure 4. Late FA with blockage along superior arcade OS (B).įigure 3. Early FA with disc hyperfluorescence and blockage along superior arcade OS (A). Fluorescein angiography (FA) showed early disc hyperfluorescence with blockage along the superior arcade without late leakage (Figure 2).įigure 2. Dilated funduscopic examination revealed clear media without inflammation OD and 3+ vitritis, optic disc hyperemia, and superior retinitis with peripheral vasculitis OS (Figure 1). Anterior segment examination OD was normal with a clear lens OS was notable for 2+ conjunctival injection and anterior chamber with 2+ cell and flare. Intraocular pressure was 14 mm Hg in each eye.
#Gonorrhea symptoms eyes full
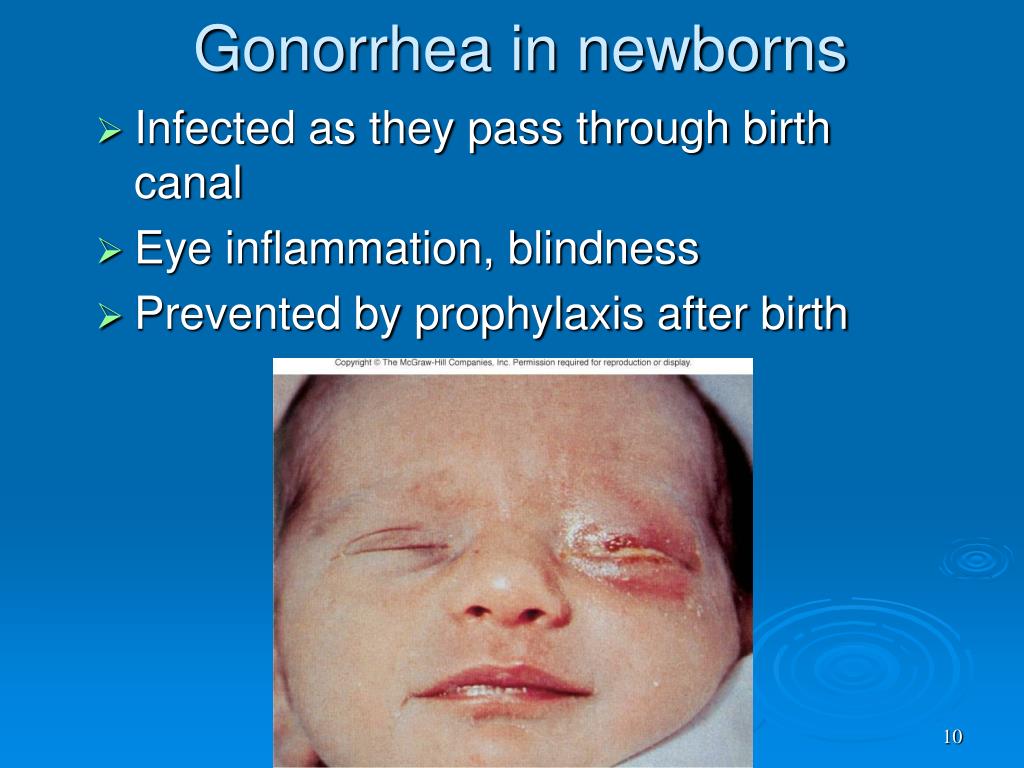
Confrontation fields were full OD and revealed an inferotemporal defect OS. His pupils were equal, round, and reactive to light. On initial presentation, his best corrected visual acuity was 20/25 OD and 20/70 OS. He reported no changes in his right eye (OD). Fundus photography OS demonstrates vitritis, disc hyperemia, and superior retinitis (B).Ī 26-year-old Filipino man with no significant medical history was referred to the retina clinic at the MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington, DC, for decreased vision in his left eye (OS) after 10 days of associated pain and redness. Fundus photography OD shows no acute findings (A). In this article, we detail the diagnosis and successful treatment of an HIV-positive patient with ocular syphilis.įigure 1. Ocular syphilis is a subtype of neurosyphilis that can be associated with uveitis, optic neuropathy, and other vision-threatening conditions. 1 Syphilis is a spirochetal bacterial sexually transmitted disease caused by Treponema pallidum, which can affect the skin, heart, blood vessels, central nervous system, bones, and eyes. The incidence of syphilis has increased in the United States over the past decade, especially in those infected with HIV. All patients with a new ocular syphilis diagnosis should be tested for HIV and screened for other common sexually transmitted diseases, specifically gonorrhea and chlamydia.Panuveitis and posterior uveitis are the most common manifestations of ocular syphilis, but other presentations have been reported.Ocular syphilis is a subtype of neurosyphilis that can be associated with uveitis, optic neuropathy, and other vision-threatening conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
